Is your system struggling to handle graphics-intensive tasks such as running video editors or playing video games? Then that’s because your PC is using up all the available VRAM. Hence, to solve it, you need to Increase the dedicated Video RAM (VRAM) in your Windows PC.
But what exactly is VRAM, how important is it for your PC, and how can you expand its capacity on your Windows PC? We have answered all your queries in this detailed guide. So, no matter your experience in technical matters, you will be able to Increase VRAM by following these easy steps.
What Is Dedicated Video RAM (VRAM)
Video RAM (VRAM) is a special type of memory that works with all the graphical tasks such as gaming and video editing, assigned to the GPU. VRAM holds information that the GPU needs so that the GPU can quickly access it and output the result. So, when you increase the dedicated Video RAM (VRAM) in your Windows PC, it will result in better processing of graphical data, making your PC run faster and smoother.
Before checking how to increase VRAM on your Windows PC, it’s good to know how much VRAM your Windows PC has. This will help you know how much Video RAM your system needs and plan accordingly. Now that you are all set, we can start looking at how you can increase dedicated GPU memory on your Windows PC.
How to Increase Dedicated Video Memory (VRAM) in Windows 10 or 11
Now that you know what is VRAM and how increasing it can help you improve the graphical performance of your system, it’s now time to look at all the ways in which you can make it possible.
1. Upgrade to a Dedicated GPU
The best way to increase the dedicated Video RAM (VRAM) on your Windows is by upgrading the Graphics card in your PC. As new graphics cards come with better VRAM with more memory capacity. However, if that’s too expensive or if you own an un-upgradable laptop, see the next few sections to increase the VRAM on your Windows PC.
2. Get More Video Memory (VRAM) Using BIOS
BIOS or UEFI is the firmware embedded in a computer’s motherboard. In modern computers, the traditional BIOS has been mostly replaced by the more advanced UEFI. However, the Windows recovery is still referred to as BIOS. It comes with a set of instructions to initialize and control various hardware components on your computer.
Hence, when you make the following changes to your system, you will be able to get more VRAM in your system. To increase the dedicated Video RAM in Windows 10 or 11 systems, you need to first enter into BIOS/UEFI. Next, follow the below steps.
Note: The steps mentioned here are for Windows 10 and 11 PCs that come with the old BIOS UI. Even in that, there might be some difference in the option names. We have tested the following steps on a Lenovo laptop that comes with the old BIOS UI.
Step 1: Once you enter the BIOS menu, go to the Configuration tab.
Tip: You can use arrow keys to navigate in BIOS.

Step 2: Go to ‘UMA Frame buffer size’ at the bottom and hit Enter.

Step 3: Now, choose the size of your choice and hit Enter
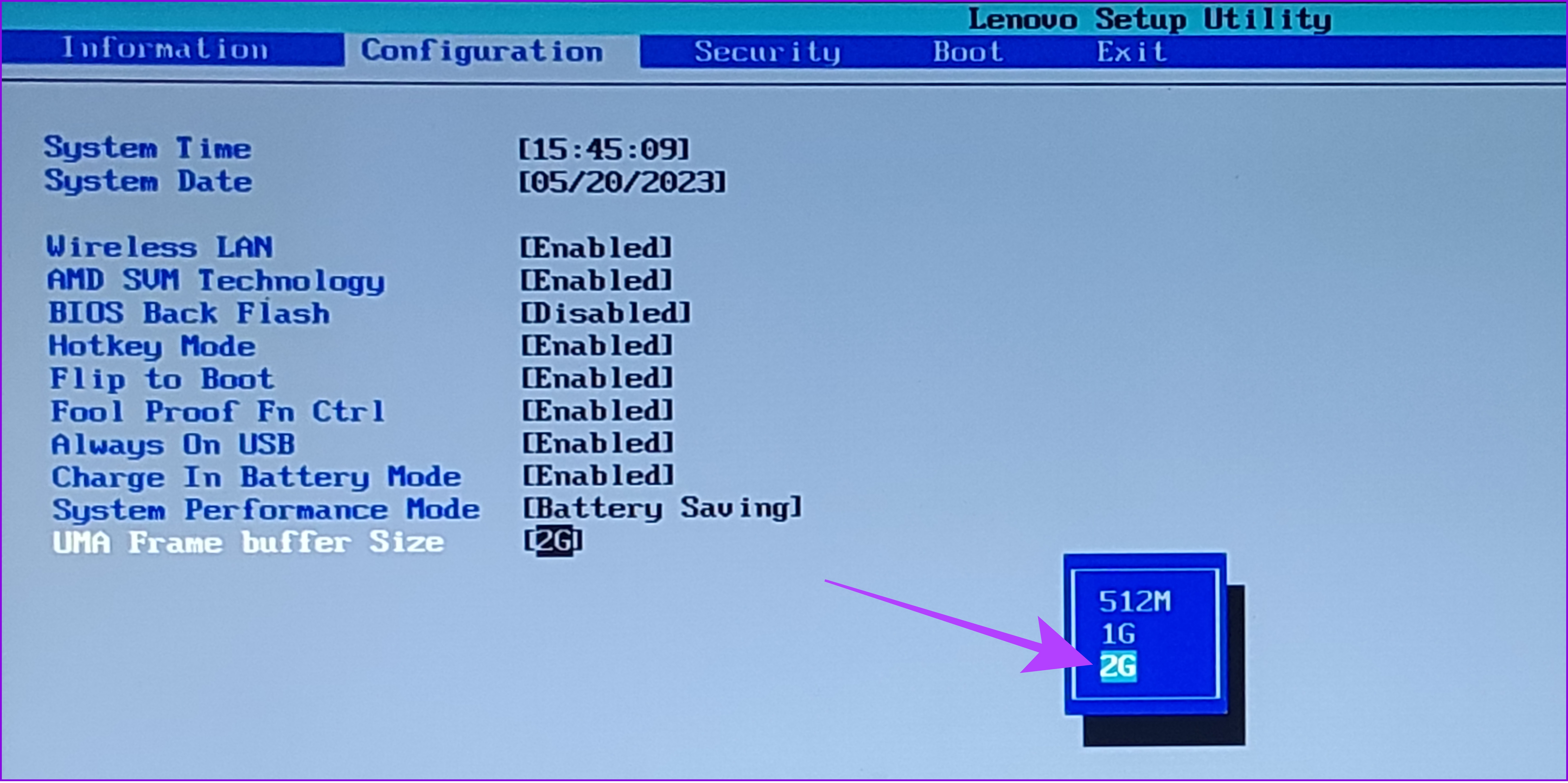
Step 4: Once you make the necessary changes, hit F10.
Step 5: Choose Yes to confirm the changes and boot back to Windows.

If you can’t see the same menu options in your Windows system, then it might be because your manufacturer shipped the system with a new recovery UI. In that case, we would suggest you check with the brand support or forum to know the right menu names.
3. Modify Value in Registry Editor
You can make many changes in your system including increasing the allocated VRAM memory. However, it doesn’t increase the Video RAM. Instead, it just modifies a dummy value with which you can fool the games that require a specific amount of VRAM to run. Additionally, since we are going to use Registry Editor, we recommend taking a back up before proceeding with the steps.
Note: Since the VRAM value is not actually changed, it might put some pressure on your system if you run applications that consume the maximum Video RAM.
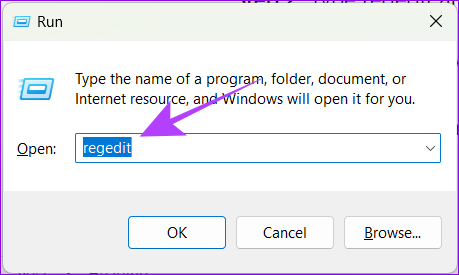
Step 1: Open Run by using the key combination Windows key + R.
Step 2: Type regedit and hit Enter.
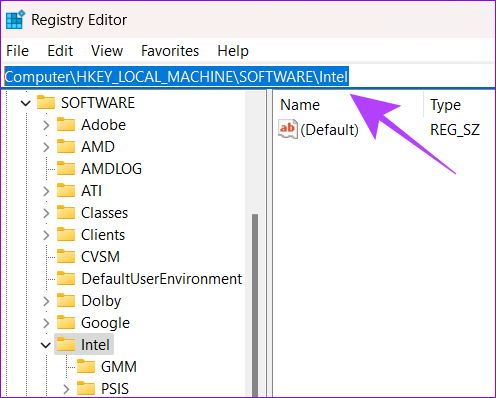
Step 3: Paste the following path and hit Enter.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Intel
Note: You can paste this step even if you have an AMD-powered Windows machine.
Step 4: Right-click the Intel folder and navigate to New > Key.
Note: If you have multiple user IDs on your Windows PC, you should perform these steps on your admin user.
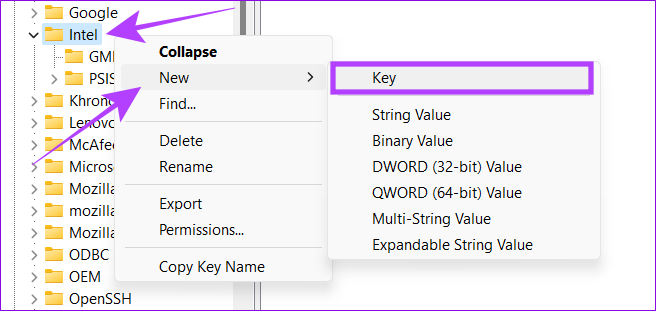
Step 5: Name the new Key as GMM.
Step 6: Choose the GMM folder and right-click on the right side.
Step 7: Select New and hit ‘DWORD (32-bit) Value’.
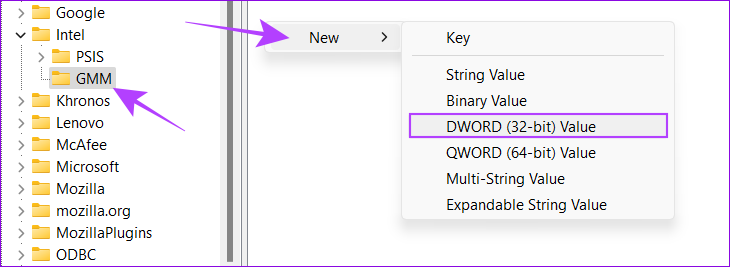
Step 8: Name it DedicatedSegmentSize.
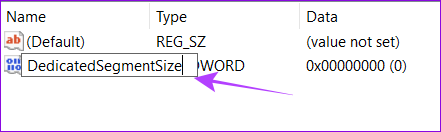
Step 9: Right-click and choose Modify.
Step 10: In the appearing pop-up, type any value between 0 and 512, choose Decimal, and hit OK.
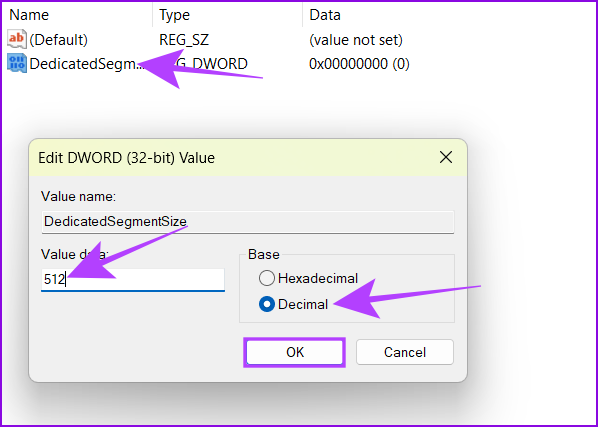
Step 11: Restart your system and see if you notice any difference.
Tip: You can increase the value if you weren’t able to notice any difference.
4. Upgrade System RAM
If there’s no dedicated video memory, or if you don’t have enough budget to upgrade the GPU, your PC will utilize the system RAM, for graphic-intensive tasks by default. Increasing the value by following the steps mentioned above will take up more RAM and might affect the general performance.
You can free up RAM on your Windows system or upgrade the default RAM so that it can be allocated for such tasks.
FAQs on Increasing Dedicated Windows VRAM
The need for VRAM varies based on the tasks you want to perform with it. Regardless, we would suggest having at least 2GB of VRAM to perform minimal gaming and other graphical tasks such as video editing or more.
You cannot download VRAM as it’s a hardware component built into your graphics card or integrated graphics of the chipset.
Enjoy Better Performance
With this guide, we hope that you were able to increase dedicated VRAM in Windows. However, we want to clarify that, despite you increase the dedicated VRAM, you will face performance issues if the GPU is not powerful enough to handle the tasks you throw at it. If you still have any doubts, suggestions or just want to say hi, the comment section is open for you.
Was this helpful?
Last updated on 20 February, 2024
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.