Method 1: Using Windows Search
Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard or click the on-screen Windows icon.
Step 2: Type Local Security Policy and click Run as administrator.

In the prompt, select Yes.
If you cannot see the search bar on your Windows PC, fix the missing search bar by following a few simple steps.
Method 2: From Windows Tool
Step 1: Press the Windows key on the keyboard or click the Windows icon on the taskbar and select All apps.
Step 2: From the list of programs, scroll down and click on Windows Tools.
Note: If you are on Windows 10, find the Windows Administrative Tool.

Step 3: Finally, click on Local Security Policy.

If you don’t want to access Windows Tools from the Start Menu, there are multiple ways to do so.
Method 3: Using File Explorer
Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard, type File Explorer, and click Open.
Step 2: Navigate to the address bar, type the below command, and hit Enter.
secpol.msc

Method 4: Using Task Manager
Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard, type Task Manager, and click Open.
Step 2: Click on Run new task.

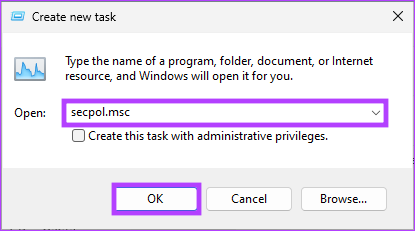
Step 3: In the Create new task window, in the text field, type secpol.msc, and click OK.
Method 5: From Run Command, Command Prompt, or PowerShell
Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard, type Command Prompt or PowerShell or Windows Terminal, and click Run as administrator.
In the prompt, select Yes.
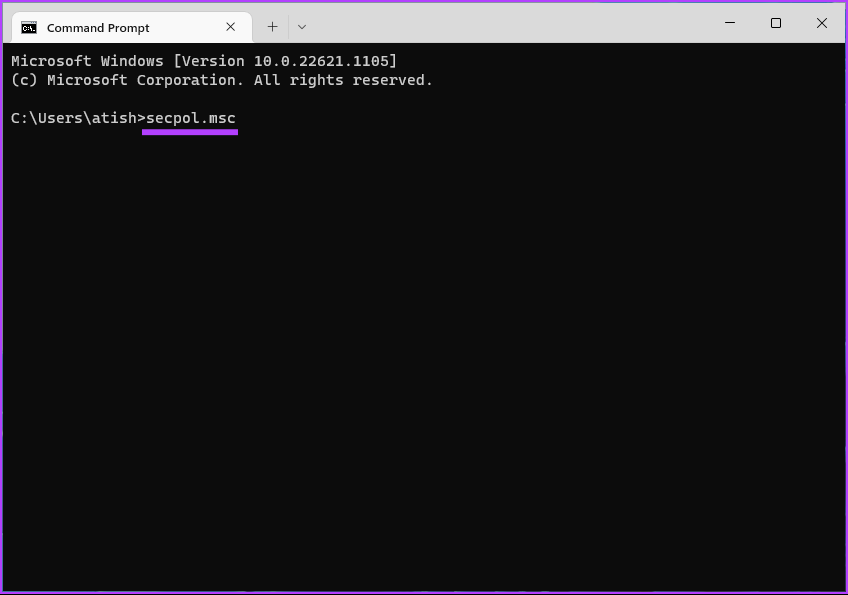
Step 2: Type the below command and hit Enter.
secpol.msc
Also Read: Top ways to back up the Local Group Policy editor on Windows 11
Method 6: Using Group Policy
Group Policy Editor is an excellent tool for managing Windows settings, including the Windows Firewall.
Step 1: Press the Windows keys on your keyboard, type gpedit, and click Open.
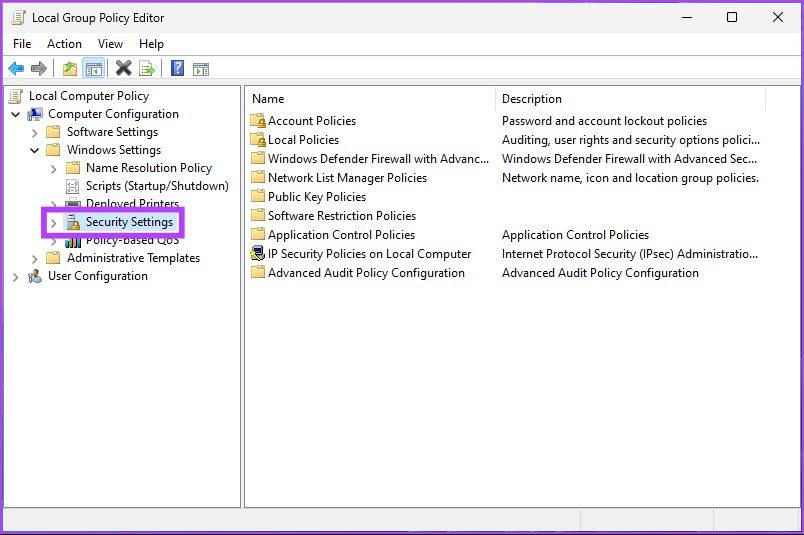
Step 2: In the left pane, under Local Computer Policy, select Computer Configuration.

Step 3: In the right pane, double-click on Windows Settings.

Step 4: Select the Security Settings option.
If you have any queries, check out the FAQ section below.
FAQs
It depends on the changes to the local security policy and the operating system being used. Some changes to the local security policy might take effect immediately, while policies such as user rights, password policies, or firewall rules may require a reboot for the changes to take effect.
It depends on the security policy and the operating system you use. System administrators are usually in charge of security policies because they have the necessary rights and permissions to do so.
Was this helpful?
Last updated on 26 April, 2024
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.